Techniques to estimate depth from image blur are known as Depth from Defocus (DfD), and has been actively studied. In this study, we utilize the projection defocus by a projector with coded aperture. The method estimates the depth by analyzing the amount of blur of reflected light pattern which is projected from projector as a dot grid pattern. In addition, we generated a coded aperture that was designed as an aperture installed in the projector and optimized for DfD by Genetic Algorithm. Advantages of this study are as follows.
- By utilizing blur effects actively, the depth can be estimated in the out-of-focus
area. In the future, the measurement rangne can be extended by combining a conventional
active 3D measurement method.
- Since the baseline between a camera and a projector is not necessary, the system can be compact.
- Measurement accuracy can be improved by using coded aperture
 Fig.1 Diagram of optical system and actual optical system
Fig.1 Diagram of optical system and actual optical system
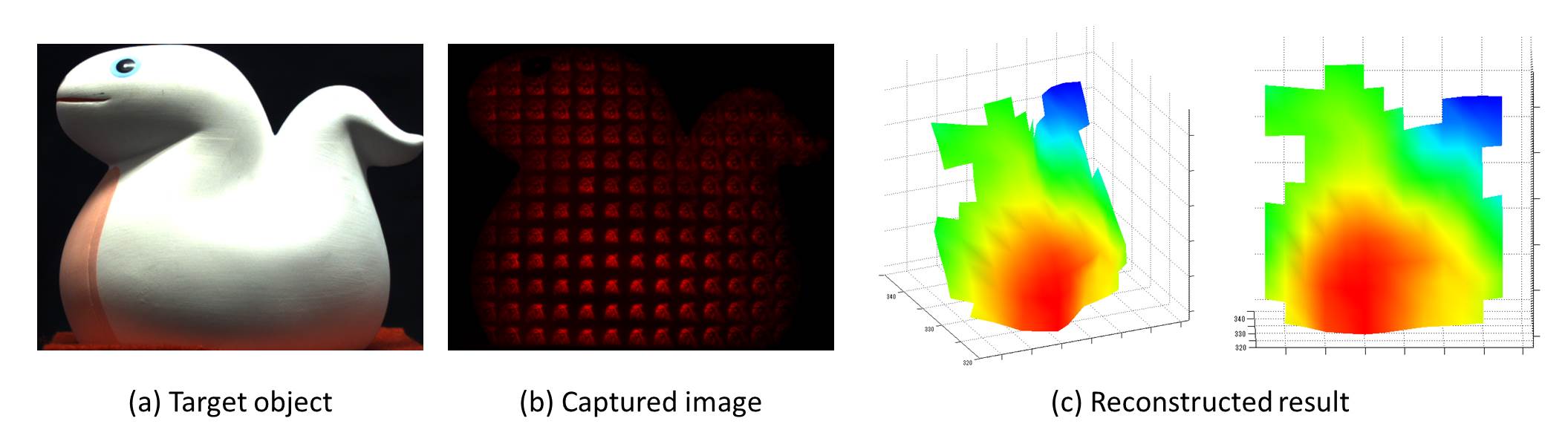 Fig.2 Arbitrary shape estimation
Fig.2 Arbitrary shape estimation
Publications
[1] Yuki Horita, Satoshi Ono, Hiroshi Kawasaki, Makoto Kimura, Yasuo Takane
"Robust active 3D measurement method against bokeh using projector-camera system with coded aperture"
IEICE Transactions on Fundamentals of Electronics, J96-D, pp.1823-1833, 8.2013
[2] Hiroshi Kawasaki, Yuki Horita, Hitoshi Masuyama, Satoshi Ono, Makoto Kimura, Yasuo Takane
"Optimized Aperture for Estimating Depth from Projector's Defocus"
International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV2013), pp.135-142, 6.2013
|

 Fig.1 Diagram of optical system and actual optical system
Fig.1 Diagram of optical system and actual optical system
 Fig.2 Arbitrary shape estimation
Fig.2 Arbitrary shape estimation